Voltage and Frequency Differences in Japan
In Japan, electricity runs on a different voltage and frequency compared with other countries.
To ensure correct and safe use of electrical appliances, this site explains the electricity system in Japan.
Kansai Electric Power supplies electricity at 100 V / 60 Hz.
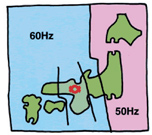
Map of regional frequency differences

Shape of 100 V and 200 V plug sockets
Although 200 V is used for some appliances, the voltage in Japan is generally 100 V.
Appliances brought from overseas might not be usable at the voltage in Japan. Note that the plug sockets for 100 V and 200 V are different in shape.
The electric frequency is different on either side of the Fujigawa River in Shizuoka Prefecture and Itoigawa City in Niigata Prefecture, with 50 Hz to the east and 60 Hz to the west. Kansai Electric’s service area uses a frequency of 60 Hz.
Some appliances cannot be used at different frequencies.
Be careful to not use electrical appliances that cannot be used at a different frequency.
Appliances that can be used in either area

Televisions and radios can be used.
Televisions, radios, etc.
Appliances that can be used but with reduced efficiency
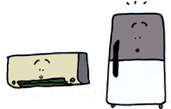
Refrigerators and air-conditioners will work, but less efficiently.
Refrigerators, electric fans, air-conditioners, etc.
Appliances that cannot be used at a different frequency area

Washing machines and microwave ovens cannot be used.
Washing machines, microwave ovens, fluorescent lights (unless an inverter- s used), clothes driers, etc.
*The appliances listed here are general examples. There are exceptions, so be sure to check the operating manual or consult with the manufacturer directly.
A Guide To Electricity
Information for Foreign Residents of Japan Menu

